Documentation
GDPR in the US: a GDPR Checklist for US Companies
Since its enforcement in 2018, one of the most asked questions about GDPR has been: does the GDPR apply outside the European Union? And, more specifically: does it apply to US companies? If yes, what are the requirements for GDPR in the US?
In this post, we’ll give you all the background information needed to answer the questions above and get a clear understanding of GDPR applied to the US. We also provide an actionable checklist for US companies, including detailed steps that they may need to take in order to comply (and avoid fines!). Let’s get started!
Short on time? Jump to… ⬇️
Does the GDPR apply to the US?
Yes, the GDPR may apply in the US, or in any country in the world. Even though it does not have jurisdiction in the United States, its provisions have an extraterritorial scope, meaning that GDPR requirements can apply outside the European Union.
The regulation is meant to protect European individuals and their data. As a result, the GDPR also extends to foreign companies that, based outside the EU, engage in specific activities involving European residents.
Article 3 of the GDPR states:
This Regulation applies to the processing of personal data in the context of the activities of an establishment of a controller or a processor in the Union, regardless of whether the processing takes place in the Union or not.
Specifically, for the GDPR to apply to your US business, you should meet at least one of the following requirements:
- Your business is based in the EU (please note that this applies even in the case of an EU-branch office); or
- You’re not based in the EU, but you offer goods or services (even for free) to EU-based users; or
- You’re not based in the EU, but you monitor the behavior of EU-based users.
In short, if you’re a US-based company, and you’re collecting, processing or storing data from individuals in the EU, you’re expected to comply with the GDPR.
💡 See an example here
Here’s a practical example, taken from the European Data Protection Board guidelines:
A start-up established in the USA, without any business presence or establishment in the EU, provides a city-mapping application for tourists. The application processes personal data concerning the location of customers using the app, in order to offer targeted advertisement for places to visit, restaurant, bars and hotels. The application is available for tourists while they visit New York, San Francisco, Toronto, Paris and Rome. The US start-up is specifically targeting individuals in the Union (namely in Paris and Rome) through offering its services to them when they are in the Union. The processing of the EU-based data subjects’ personal data together with the offering of the service falls within the scope of the GDPR. Furthermore, by processing data subject’s location data in order to offer targeted advertisement, the processing activities also relate to the monitoring of behavior of individuals in the Union. The US start-up processing therefore also falls within the scope of the GDPR
Does the GDPR apply to US citizens?
Yes, the GDPR applies to US citizens that are physically located in the European Union. It applies to any individual, regardless of nationality, as long as they are physically located in the European Economic Area (EEA) at the time their personal data is processed.
For example, if a US citizen visits France on vacation and uses an app to buy train tickets, the GDPR applies because their personal data is processed within the EU. The regulation is territorial, meaning it protects the data of individuals based on their location, not their citizenship.
Does the GDPR apply to EU citizens in the US?
In most cases, the GDPR does not apply to EU citizens while they are in the United States, because the regulation primarily protects individuals who are located in the EEA at the time of data processing.
However, there are exceptions. The GDPR may still apply if:
- An EU-based company processes the data of an EU citizen in the US (e.g., an EU bank handling an EU citizen’s account).
- A US company processes an EU citizen’s data on behalf of an EU-based organization.
- The data was originally collected in the EU and continues to be subject to GDPR rules.
While the GDPR does not automatically follow EU citizens wherever they go, it can still apply in specific cases, particularly when EU-based entities or services subject to the GDPR are involved in processing their data.
🇬🇧 Do US companies have to comply with UK GDPR?
The UK GDPR is the UK equivalent of the General Data Protection Regulations, which was enforced after Brexit.
As the EU GDPR, the UK GDPR also applies outside the UK if you:
- offer goods or services to individuals in the UK; or
- monitor the behavior of individuals taking place in the UK.
If your US business falls into one of these categories, then you need to comply with the UK GDPR as well.
Who enforces GDPR in the US?
The GDPR in the US is typically enforced by Data Protection Authorities (or DPAs), which are independent public authorities established in each EU member state. It is not enforced by any US agency or authority because it is a European Union regulation, even though its reach extends outside the EU.
DPAs supervise the application of the GDPR within their respective territories. They also conduct investigations, issue hefty fines and sanctions, and provide guidance on best practices for complying with the GDPR and relevant national laws. There is one in each EU Member State, for instance in France it is called the “CNIL” or in Italy the “Garante”.
If a US-based company is in violation of GDPR, the lead on enforcement action is generally taken by the DPA of the EU member state where the violation occurred, or where the affected EU residents reside.
In case the US company has some headquarters within an EU Member State, the DPA of that specific state becomes the primary or lead regulator for that business. This DPA would be responsible for coordinating any enforcement actions with its counterparts in other EU states where violations may have occurred.
What is the GDPR equivalent in the US?
There is no GDPR equivalent in the US, meaning there isn’t a single federal law that is similar to the GDPR.
A federal act, the American Privacy Rights Act, has been proposed, but it’s still under discussion and not finalized yet.
However, some states have privacy laws, such as the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), that usually apply only to residents of that particular state.
In the last years, a growing number of US states have implemented new privacy laws like Virginia and the VCDPA, Colorado and the CPA, Utah and the UCPA or Connecticut and the CTDPA, in a common effort to have a framework in place for data privacy.
None of the US state privacy laws are as comprehensive as the GDPR yet, but they help protect, grant consumer rights and introduce legal requirements for companies that process personal data of residents of the state. For example, businesses are required to include specific disclosures in a privacy policy or display a notice to inform consumers of data collection practices.
The country also has some sector-specific laws governing different types of data and industries, like HIPAA that regulates healthcare data or the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act for financial data, enforced by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
🇺🇸 More on US State Privacy Laws
The CPRA (California) and the VCDPA (Virginia) became effective on January 1, 2023.
The CPA (Colorado) and CTDPA (Connecticut) on July 1, 2023.
The UCPA (Utah) on December 31, 2023.
These US laws require, among others, that you:
- Provide your users with a privacy policy including specific details. For example, you need to disclose some additional information, such as users’ rights and describe your data processing practices.
- Enable your users to opt out of the processing for certain purposes (sale, targeted advertising and sharing, among others).
- VCDPA, CTDPA, and CPA only: Enable your users to opt in to the processing of their sensitive data.
- CPRA only: Show users the required notice at collection to inform them about the categories of personal information that are collected, the purposes of collection, and whether this information is sold or shared.
For a recap overview, take a look at this video:
How can the GDPR affect US companies?
As we’ve demonstrated above, it’s a mistake to think that, since the GDPR is a European regulation, it doesn’t affect US businesses at all.
Overall, it is strongly recommended for US companies to assess their data processing activities and consult legal experts to determine if compliance to the GDPR in the US is required in their specific situation.
Penalties for non-compliance to GDPR in the US can be significant. They can be monetary, or not:
- Fines can go up to EUR 20 million (€20m) or 4% of the annual worldwide turnover (whichever is greater).
- Equally concerning are the other potential sanctions: official reprimands (for first-time violations), periodic data protection audits and liability damages.
💡 Take this 1-min quiz to find out which laws are relevant to you!
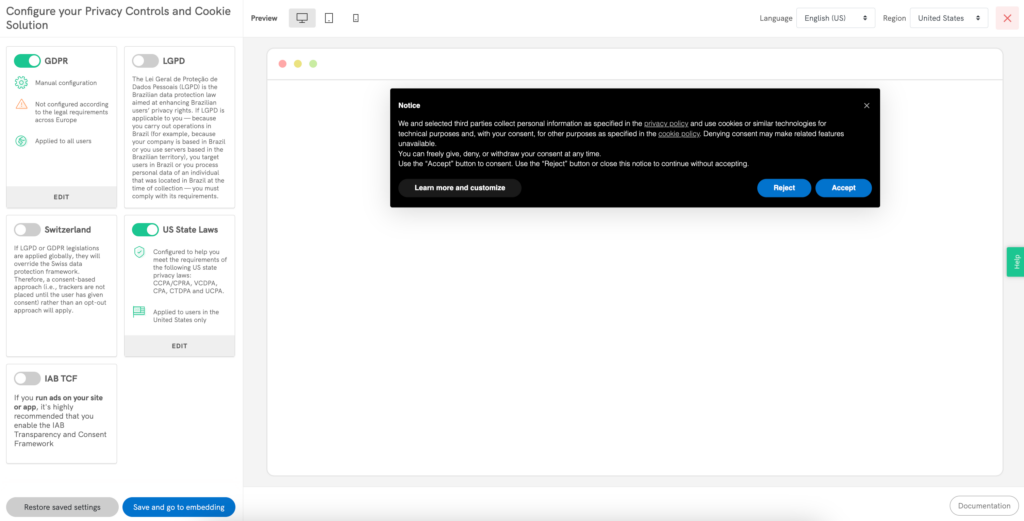
Did you know you can comply with both US Privacy Laws and the GDPR at the same time?
With iubenda, simply select which region you are based in, then where your users are based, and our solution does the rest! It suggests a configuration that will allow you to comply with all applicable regulations.
GDPR in the US: Main Requirements
As a US-based business, here are the main GDPR requirements you must follow.
Have a lawful basis
Before you can collect or process any personal data, the GDPR mandates that you have at least one lawful basis for doing so. These lawful bases are:
- The user has given consent for one or more specific purposes.
- The data processing is necessary for the performance of a contract or in order to take steps prior to entering the contract.
- Other legal bases include: the processing is necessary for fulfilling a legal obligation OR protecting the vital interests of a person OR for performing a task carried out in the interest of the public OR for the legitimate interests of the data controller or third party.
💡 You must identify and document the lawful basis for each specific data processing activity you undertake.
Make legally required disclosures via your privacy policy
GDPR compliance in the US requires you to provide your users with a privacy policy, where you include all the details regarding your data processing activities.
Under the GDPR, your privacy policy should at least include:
- Who is the site/app owner?
- What data is being collected and how?
- What is the Legal basis for the collection?
- Why are you collecting the data?
- Are there any third parties involved in the processing? If yes, what are they?
- Do you transfer data abroad? If yes, what security measures are in place to safeguard the data?
- What rights do users have? How can they exercise them?
- How will you notify your users of any changes in the policy?
- The effective date of the policy.
💡 Remember to add your privacy policy where it’s easily accessible, for example in the footer of your website. You can learn more here: What is a Privacy Policy and Do You Need One?
Acquire verifiable consent
While US legislations typically allow the collection and processing of personal data without obtaining the user’s prior consent, the GDPR requires that you collect “freely given, specific, informed and explicit” consent through a clear “opt-in”, or positive action.
This essentially means that before collecting any of the individual’s personal data on your site via cookies or via a form for example, you must ask for their consent. This mechanism must be unambiguous; “opt-out” mechanisms like pre-ticked boxes are forbidden.
You should also grant users the right to withdraw consent. It must be as easy to withdraw consent as it is to give it. To learn more about the rights of European residents under the GDPR, read this guide.
💡 Your consent forms must be straightforward, easy to understand and conspicuous. Individuals should actively opt in.
Keep clear records related to the consent
Consent, under the GDPR, is paramount. The regulation requires meticulous record-keeping related to what information was disclosed, how the consent was obtained (e.g. via a website form), and when it was obtained.
Companies need to maintain clear consent records that can prove that individuals provided informed consent. This adds a complex administrative layer but is essential for compliance.
💡 As you can imagine, this is not an easy task! That’s why we recommend using a Consent Database.
Assess cross-border data transfers between the EU and the US
GDPR in the US allows data transfers of EU residents’ data outside of the European Economic Area (EEA) only when certain set conditions are met.
Under GDPR requirements, the country or region the data is being transferred to must have an “adequate” level of personal data protection by EU standards, or where not considered adequate, transfers may still be allowed under the use of standard contractual clauses (SCCs) or binding corporate rules (BCRs).
A decision was taken on the EU-US Data Privacy Framework on July 10, 2023 and declared that the United States is recognized as providing an adequate level of protection to its European Union (EU) counterpart. Consequently, personal data can now flow freely from the EU to US self-certified companies without the need for additional safeguards.
EU-US data transfers are allowed for US organizations that have been certified. If you wish to do so, you need to meet the privacy principles outlined in the Data Privacy Framework and only then your company will be added to the DPF list.
👉 Here’s how to self-certify
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
If you’re based outside the EU, you may still need a European representative to ensure your company is complying with the GDPR. This person is called a Data Protection Officer, or DPO, and is in charge of ensuring that personal data is processed following the applicable data protection rules.
However, the appointment of a DPO is not always mandatory, it depends on the scale and nature of data processing activities. Specifically, you need to appoint a DPO when:
- There is large-scale regular and systematic monitoring of users (for example, processing with video surveillance systems).
- The processing is carried out by a public authority (except for courts or independent judicial authorities).
- The organization is performing complex operations with user data (in particular sensitive user data).
💡Are you selecting a DPO? Here’s what to look for.
Carry out a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
For data processing activities that are likely to result in high risks to individuals, the GDPR requires a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) to be carried out. This is an assessment that evaluates how personal data is processed and how to mitigate risks to data subjects.
This involves identifying the nature, scope, context, and purpose of the data processing, assessing the risks to individuals, and identifying measures to mitigate those risks.
GDPR Compliance Checklist for US Companies

Here’s a practical checklist to help you navigate GDPR compliance as a US-based business.
⬇️ So, how can you get started right away and check most of the boxes above in just a few minutes?
How iubenda can help with GDPR in the US
Reading all this can be quite overwhelming. We get it. It’s technically and legally complex.
But, fear not, we know exactly what you need.
iubenda provides comprehensive attorney-level compliance software solutions that can help you comply with GDPR in the US.
🚀 Full GDPR compliance, but not only! Make your websites and apps compliant with the law across multiple countries and legislations.
🚀 Be safe and lower the risk of fines: we built our solutions with the strictest regulations in mind.
🚀 100% customizable: generate your own privacy policy and customized consent banner!
🇺🇸🇪🇺 Comply with US and European laws simultaneously
Global compliance is just one click away.
With iubenda’s Privacy Controls and Cookie Solution, generate a customizable location-based consent banner.
The right consent parameters, text, privacy policy link and language will apply to the right users automatically. Yes, it’s that easy!